NEWS AND UPDATES
The latest updates regarding our products and our company
What is a laboratory sample pulverizer and how does it work?
In the world of material testing, a laboratory sample pulverizer plays a crucial role. According to Dr. James Thompson, an expert in material analysis, "The efficiency of a laboratory sample pulverizer depends on its design and maintenance." This powerful equipment is designed to grind various materials into finer particles for analysis.
laboratory sample pulverizers come in different styles and sizes. Some use mechanical force, while others rely on high-speed rotation. Each type has its unique benefits and challenges. Moreover, the precision of sample preparation is vital for accurate test results. However, this precision can be compromised by improper use or maintenance.
The importance of the laboratory sample pulverizer cannot be overstated. It ensures that materials are adequately prepared for testing, ultimately impacting research outcomes. Yet, many users overlook critical maintenance steps. Reflecting on best practices can improve the efficiency and longevity of these essential tools.
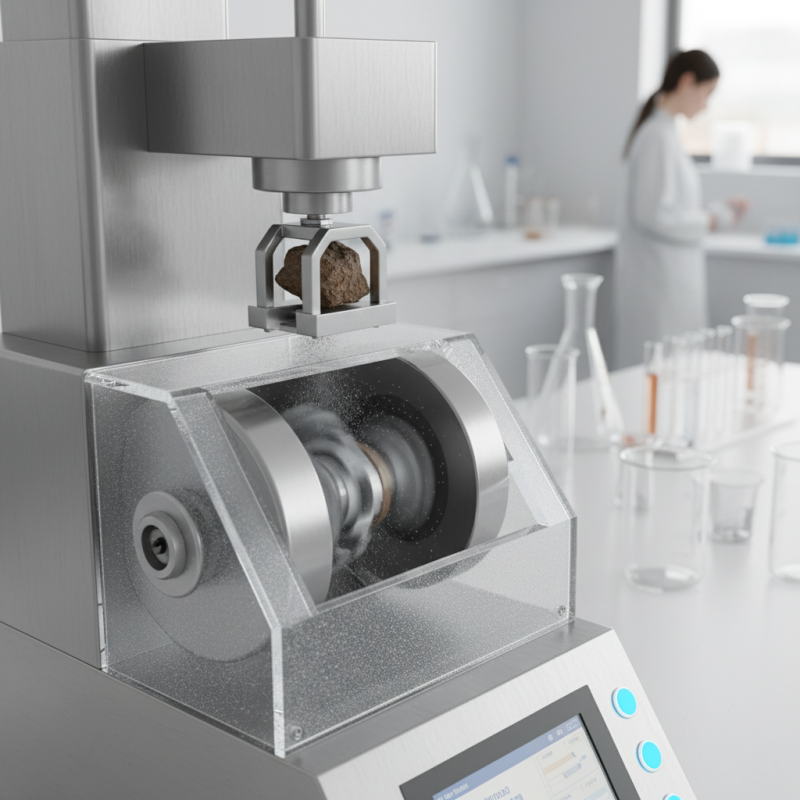

What is a Laboratory Sample Pulverizer?
A laboratory sample pulverizer is a critical tool in analytical laboratories. It is designed to reduce materials to a fine particle size for accurate testing. This equipment plays an important role in various industries, including mining, pharmaceuticals, and materials science. According to industry reports, sample preparation can significantly influence test results, making the pulverizer essential.
The pulverizer works through mechanical action. It crushes and grinds samples using force and friction. Depending on the material, operators can adjust the grinding parameters. The process ensures uniformity and enhances the accuracy of subsequent analyses. A study indicated that sample size and preparation methods can alter results by up to 30%. This highlights the importance of using the right pulverizing techniques.
Tips: When using a pulverizer, always check for wear and tear. Regular maintenance can prolong its lifespan and improve performance. Additionally, ensure the samples are dry for more consistent results. It’s crucial to clean the equipment thoroughly after each use to avoid contamination. Neglecting these practices could lead to erroneous conclusions from your tests.
The Importance of Laboratory Sample Pulverizers in Scientific Research
Laboratory sample pulverizers play a crucial role in scientific research. They help scientists prepare samples by grinding them into fine particles. This process is essential for accurate analysis. When samples are finely ground, they react more uniformly with chemicals. Such uniformity leads to more reliable results in experiments.
Tips: Always ensure the pulverizer is clean before use. Residue from previous samples can contaminate new ones. Regular maintenance is necessary to keep the equipment working efficiently.
The importance of these machines cannot be overstated. They are vital for studies in various fields, such as geology and chemistry. A poorly ground sample may lead to flawed results. Scientists must pay close attention to the grain size of the pulverized material. A consistent particle size ensures that analyses are reproducible and valid.
Tips: When setting up your pulverizer, calibrate the settings carefully. Different materials may require different approaches. Understanding the material properties is key to successful pulverization.
How Laboratory Sample Pulverizers Operate: A Step-by-Step Guide
Laboratory sample pulverizers are essential tools in various industries. They reduce samples to a fine powder, preparing them for analysis. The process starts with placing the sample into the pulverizer's chamber. Compressive forces then crush the material against a hard surface. This action efficiently breaks down the sample to the desired particle size. Grain sizes can vary dramatically, often reducing materials to less than 0.1 mm.
The effectiveness of a laboratory pulverizer depends on design. Many models utilize rotating grinding elements to achieve consistent results. According to industry reports, over 60% of laboratories rely on pulverizers for accurate sample preparation. This is crucial in fields like mining and pharmaceuticals, where precise material characterization matters. However, achieving uniformity is not always guaranteed. Variations in sample hardness can lead to inconsistent results.
Additionally, operators must monitor machine settings closely. If not, the pulverization process may produce particles that are too large or uneven. Some reports indicate almost 15% of samples fail to meet quality checks due to improper pulverization. This calls for operators to engage in regular maintenance and calibration. Keeping equipment in optimal condition reduces failures and improves sample accuracy significantly.
Laboratory Sample Pulverizer Performance Analysis
Types of Laboratory Sample Pulverizers and Their Applications
Laboratory sample pulverizers play a crucial role in material analysis. Different types ensure versatility across various applications. The most common types include ball mills, disc mills, and hammer mills. Each provides unique benefits based on the material and desired fineness.
Ball mills use steel balls to crush and grind samples. They are effective for reducing materials to a fine powder. However, they require careful management of the milling time to avoid overheating the samples. Disc mills feature two grinding plates, achieving a precise particle size. They are ideal for brittle materials but may not work well with tougher samples. Hammer mills break down samples through high-speed impacts. This process is quick but can lead to uneven size distributions.
Each pulverizer type has strengths and weaknesses. Some may be better suited to specific materials, while others may struggle. A careful selection process is essential for consistent results. Operators should be aware of these factors to optimize sample processing. Understanding the limitations can lead to improvements in future applications. It’s about finding that balance between efficiency and precision.
Maintenance and Best Practices for Laboratory Sample Pulverizers
Laboratory sample pulverizers are essential tools in many scientific fields. They help prepare samples for various analyses. To maintain these machines, regular check-ups are crucial. This includes routine cleaning and inspection of components. A 2020 industry report highlighted that over 30% of equipment failures stem from insufficient maintenance. Failing to address minor issues can lead to costly repairs.
Proper operating techniques can enhance the lifespan of pulverizers. Operators should adhere to specific guidelines when feeding materials. Overloading can stress the machine. As a general rule, only fill the chamber to about 75% capacity. This measure can improve efficiency and reduce wear. Clear communication among team members is important, too. Misunderstandings can lead to mistakes that might damage the equipment.
Attention to detail in scheduling maintenance is vital. Cleaning the grinding chamber and checking fasteners can prevent accidents. Nearly 50% of laboratory accidents involve equipment failure due to lack of upkeep. Regularly reviewing techniques can identify areas for improvement. Inadequate practices might sometimes go unnoticed but can impact results significantly. Investing in proper maintenance is crucial for achieving reliable outcomes.
What is a laboratory sample pulverizer and how does it work? - Maintenance and Best Practices for Laboratory Sample Pulverizers
| Sample Type | Recommended Equipment | Optimal Grinding Speed (RPM) | Maintenance Frequency | Best Practices |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minerals | Jaw Crusher, Disk Mill | 300 - 1000 | Weekly | Regular calibration and wear part inspection |
| Biological Samples | Cryogenic Pulverizer, Ball Mill | 500 - 1200 | Daily | Utilize dry ice during processing |
| Soil Samples | Hammer Mill, Ring Mill | 400 - 800 | Monthly | Ensure sample consistency and moisture control |
| Food Samples | Grinder, Blade Mill | 300 - 900 | Bi-weekly | Keep equipment clean; avoid cross-contamination |
Article Source:
Schedule
Monday to Thursday:
8:15 – 17:00
Friday:
8:00-15:00
Address
Leonardo Da Vinci, 10
Valencia Technology Park
46980 Paterna, Valencia, SPAIN
Real Laboratory SL
info@site_e1c8a3bd-d539-4d7f-8695-37f21373de39
Teléfono: +34 96 136 61 07
